Picking the Brain
These clever facts about the body's headquarters may blow your mind.

As the control center for the body’s nervous system, the brain participates in every human function. From sensing to controlling motor skills, its vital role in movement means this cognitive powerhouse is—literally—the brains behind your work as a fitness professional.
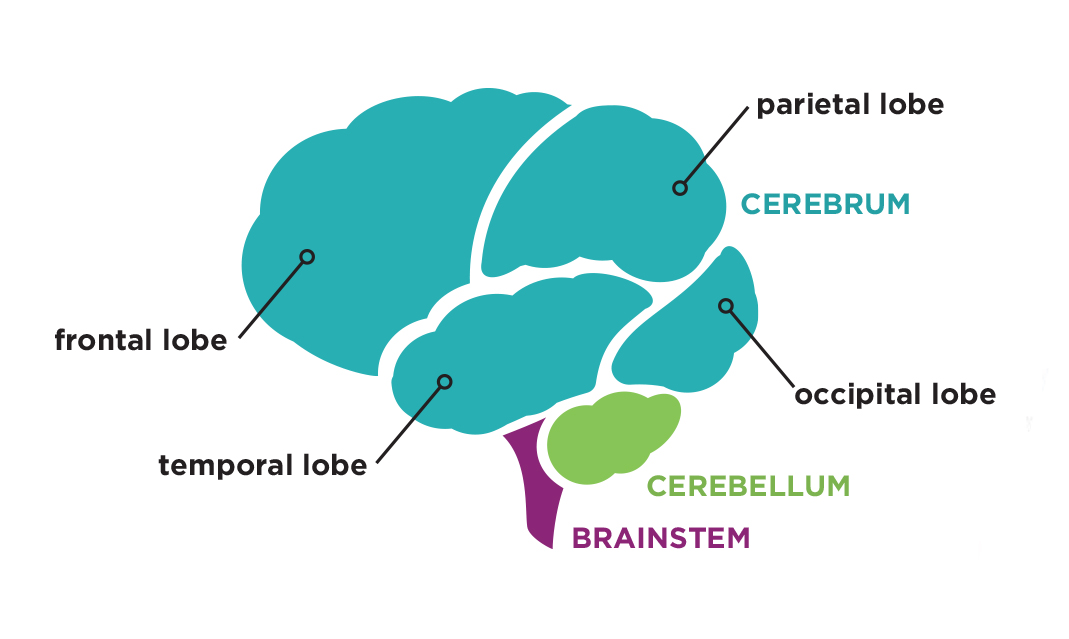
There are three main components that make up your mind:
- The cerebrum, the largest part of the brain, performs higher functions like speech, memory, reasoning, learning, emotions and receiving input from the five senses. The cerebrum is divided into two hemispheres, left and right, each of which is divided into four lobes: frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital. Every component serves a specific function and works in a complex relationship with the others.
- The cerebellum, located beneath the cerebrum, coordinates muscle movement, posture and balance.
- The brainstem connects the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord, transmitting information between the brain and body. The brainstem controls automatic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, body temperature, sleep-wake cycles and digestion.
(Sources: AANS 2019; Mayfield Clinic 2018.)
Below are more facts to keep in mind:
- The human brain weighs about 3 pounds and contains roughly 86 billion neurons, cells that transmit information through electrical and chemical signals (Lewis 2018; Mayfield Clinic 2018).
- It takes the brain 1/10,000th of a second to respond to stimuli and generate an action (Sinrich 2019).
- Damage to certain parts of the brain can cause aphasia, or loss of ability to understand or express speech. For example, injury to the Broca’s area in the left frontal lobe interferes with movement of the tongue or facial muscles, inhibiting speech. Damage to the Wernicke’s area in the left temporal lobe prevents comprehension or creation of intelligible speech, causing sound without meaning (Mayfield Clinic 2018).
- Foods that support brain health include fruits and vegetables with dark skins—like broccoli, blueberries and sweet potatoes—fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and walnuts and pecans (Burgess 2018).
- The brain is 60% fat, which stabilizes cell walls in the brain and carries, absorbs and stores fat-soluble vitamins in the bloodstream (Sinrich 2019).
- The blood-brain barrier is a protective layer of tightly bound cells that allows oxygen and nutrients to enter the brain but prevents toxins from passing through—so that harmful substances don’t cross your mind (Zuckerman 2009).
- Emerging research shows that regular exercise can support brain health by improving brain network connectivity and reducing cognitive impairment (Cohut 2019).
References
AANS (American Association of Neurological Surgeons). 2019. Anatomy of the brain. Accessed Aug. 22, 2019: www.aans.org/en/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Anatomy-of-the-Brain.Burgess, L. 2018. What percentage of our brain do we use? Medic
Sarah Kolvas
Sarah Kolvas is the content manager for IDEA.