Anatomy/Kinesiology
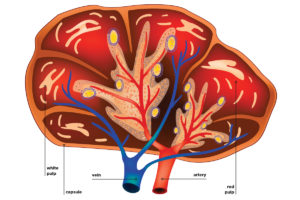
Screening the Spleen
Though known for being a nonessential organ, the spleen plays a significant role in immunity and blood health as the blood’s filtration mechanism.
Power Up Your Aging Clients
With a tailored regimen that includes muscular power training, adults can keep their bodies fit and functional well into their later years.
2 Great Exercises for an Ageless, Pain-Free Body
Whether. you’re training an athlete or an ageless warrior, keeping the feet and back healthy leads to better performance and longevity.
Why Men Breathe More Easily Than Women When Exercising
Women, on average, have a more difficult time breathing during vigorous exercise because their airways are smaller, according to The FASEB Journal.
How to Lose Weight Without Losing Bone
Wearing a weighted vest may help older adults to successfully lose weight while protecting bone quality and density.
Movement Levels Predict Heart Disease and Death
Not only can physical activity levels predict the death risk among older adults but high levels can mitigate the risk of dying from hardened arteries.
Training Toward Fleet Feet
Fitness professionals understand how critical functional feet are for training. After all, the feet and ankles act as “shock absorbers” for the body.
Mitochondria: Unpacking Cellular Power
Mitochondria are found in every cell of the human body, except red blood cells. These energy-producing organelles play a key role in exercise performance.
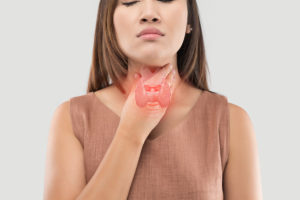
Thanking the Thyroid
Part of the endocrine system, this butterfly-shaped gland secretes hormones into the bloodstream as directed by the pituitary gland.
Not Training to Muscle Failure May Enhance Muscle Endurance
Researchers found that not performing repetitions to failure may be more effective at increasing muscle size and endurance in untrained individuals.
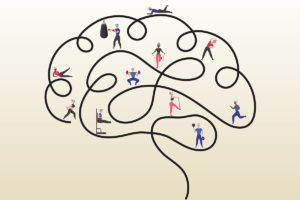
Brain Fitness Versus Physical Fitness for Healthy Aging
Cognitive capacities influence physical activity levels more than vice versa, so people with healthier brain functioning are more likely to be active.
Compound Lower-Body Exercises Build More Strength
Lower-body and multijoint exercises appear to be more appropriate for developing maximal strength than single-joint, isolated, upper-body exercises.
On Your Nerves
Talking about the nervous system may bring to mind rapid bodily responses to stress, but there’s more to this intricate bundle of fibers.
Gait Analysis in Your Shoe
Do you include gait analysis in your assessments to help you craft the perfect program? A new technology may simplify the process.
Pelvic-Floor Exercise Training and Prenatal Exercise Programs
Polish researchers evaluated the effects of adding pelvic-floor muscle education and training to a prenatal high-/low-impact exercise program.
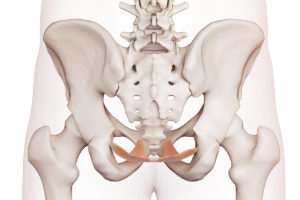
Sizing Up the Sartorius Muscle
You may not be familiar with the sartorius muscle, but you’ve no doubt flexed it during countless lower-body exercises, stretches and yoga poses.
Muscle: Use It or Lose It Until You Use It Again
It turns out we may be able to “bank” muscular training benefits from our younger selves to help maintain muscular strength as we age. One caveat: We must train again to reap those benefits.
Some Physical Activity May Not Benefit Heart Health
Resistance training may reduce fat levels around the heart (above), but not all strength-based activities are beneficial for cardiovascular health. New research shows that occupational activities like routinely carrying heavy loads at work may have a negative impact on the heart.
Strength Training Reduces Heart Fat
Location matters with body fat. The accumulation of excess fat around the heart can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. A new study by researchers at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark assigned participants to resistance training, high-intensity interval endurance training (HIIT) or no exercise. Results showed that only people who lifted weights decreased the fat lying closest to the heart—specifically, inside the sac that encases the heart (the pericardium).
Build Fitness Without Demolishing Joints
High-impact exercises — such as burpees, jumping jacks and other moves that get both feet off the ground simultaneously — can help build strength and endurance and shed fat quickly.
As a result, they’re often incorporated into high-intensity interval training (HIIT) workouts, which have gained recognition because they burn an impressive number of calories in a short amount of time and boost metabolism for up to 48 hours after the workout’s over through the afterburn effect.