Fitness Assessment
Question of the Month
When you offer training advice to clients, are you discussing the significance of sleep? If yes, are you using sleep trackers and monitoring results? Please describe how you are educating clients regarding the role of sleep in effective training and weight management and share any success stories you have had.
Share your responses with executive editor Joy Keller, [email protected].
Equal Calories Burned ≠ Same Results
Many people fixate on the number of exercise calories they burn. New research, sponsored by Les Mills International, shows that even when two group fitness activities (indoor cycling and a resistance workout) were matched for duration and caloric expenditure, they did not have equivalent metabolic effects—which could influence long-term training results. Lead study author Nigel Harris, PhD, said, “The type of exercise used to burn those calories . . . impacts the long-term positive effects that exercise has on the body.”
Tennis: Reduce Pain, Improve Performance
Tennis is one of the most popular sports in the world. In the U.S. alone, there are almost 18 million players, with another 14 million expressing interest (TIA 2018). Unfortunately, the dynamic, forceful twists and turns of the game pose ever-present injury risks to players (Roetert & Kovacs 2011).
If your fitness clientele includes people interested in playing this sport, you need to understand the causes of tennis-related injuries. This will help you develop strategies to improve movement function, reduce pain and keep clients on the court.
A for Effort
client: Kent Denver School Students | personal trainer: Laura Bordeaux, strength and conditioning coach, Kent Denver School location: Englewood, Colorado
A complete course load. Think of it as core curriculum—literally. The Kent Denver School, a college-preparatory institution outside of Denver, offers a comprehensive educational experience that emphasizes both academics and sports. That’s where Laura Bordeaux comes in.
Stand Up to Aging
Getting up off the ground grows more difficult as we age. Muscles and bones weaken, coordination becomes less fluid, and simply doing chores around the house gets more challenging. Ground-to-standing (G2S) exercises address these changes. hile even performance athletes can benefit from G2S drills (see the sidebar “G2S Exercises Also Help Performance Athletes”), they’re supremely helpful for older exercisers who are at risk for broken hips and other threats to their mobility.
High-Intensity Interval Training for Fat Loss
Two recent studies reveal that high-intensity interval training has the ability to produce high-impact fitness gains in a short time frame.
Bone Loss: A Primer
Bone loss is a normal part of aging, and understanding it can help fitness professionals to develop preventive strategies for their clients.
Walking Speed: A Predictor of Functional Health
Slow walking speed has been linked to a greater risk of mortality in older adults, while brisk walking has been linked to better health.
Spotting and Fixing Flaws in Walking Biomechanics
Participating in a program of regular exercise is a good idea at any stage of life, but particularly as we get older. Exercising frequently and consistently has many documented benefits, including promoting good health, preventing disease, enhancing mental health and physical capacity, aiding recovery from injury and illness, minimizing the effects of aging, and improving one’s ability to handle the physical demands of life (Bird, Smith & James 1998).
Exercise Doesn’t Have To Be Strenuous To Be Effective
We know that replacing sedentary behavior with physical activity yields numerous benefits. And while high-intensity models are touted as a way to fast-track success, a new study out of Sweden says it’s not necessary to go all-out in order to boost health.
Location Is Everything When It Comes to BMI
The results are in: According to a new study, people who live within close proximity to a gym or activity center weigh less than those who don’t. Access to fast-food restaurants may also affect weight, say the study’s authors.
The Best Exercise for Alzheimer’s Disease
If you were asked to choose among cardiovascular exercise, resistance training and a combination of both to help people with Alzheimer’s disease, what choice would you make?
Researchers from the University of Connecticut wanted to understand the effects of exercise—if any—on cognitive decline in those at risk of or diagnosed with Alzheimer’s. The scientists performed a meta-analysis of 19 studies (23 exercise interventions) featuring 1,145 adults aged 77 ± 7.5 years.
Secrets of Muscle Growth
Muscle growth is often a goal for people seeking guidance from qualified fitness professionals. Recently, researchers from the University of Cumbria in Lancaster, England, reviewed relevant scientific papers to find best practices for achieving that goal.
The review authors looked at several primary factors associated with muscle hypertrophy: training volume, load, training frequency, training to momentary muscle failure, exercise variation, contraction type, exercise order, repetition tempo and interest recovery. Here’s a sampling of the conclusions:
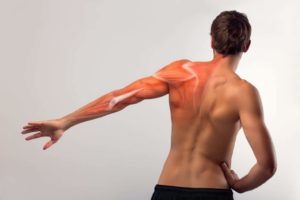
Shoulder Blades: The Right Moves
The shoulder blades, or scapulae, are critical links in the kinetic chain from the waist through the shoulders, up to the neck and down to the fingertips. Abnormalities in the position or movement of the shoulder blades—technically called scapular dyskinesis—can trigger pain and discomfort, especially among people who spend long hours sitting and using computers.
Programming to Prevent ACL Injury
Your new client, 16-year-old Alexis, is a competitive athlete who wants you to design a fitness program that will help her prevent a second anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear. She partially tore her ACL while playing soccer and rehabbed it with a physical therapist, who cleared her to play again. Alexis returned to spring softball without an issue, but she would like to be as fully prepared as possible for the upcoming fall soccer season. She hopes to be recruited to play in college, but her parents are concerned she will sustain another ACL injury, perhaps a more severe one.
Range of Motion: Full or Partial?
Research shows there’s a time and place for both full and partial range of motion in resistance training program design.
Some training systems purposely use partial ROM for various exercises. Moreover, certain surgeries and orthopedic injuries require partial-ROM movements during rehabilitation (Pinto et al. 2012). It seems natural for personal trainers to wonder which is superior: full ROM or partial ROM? ,/p>
Two studies comparing the benefits of partial ROM and full ROM give a clearer view of the landscape.
Getting to the Bottom: The Ischial Tuberosity
The posterior aspect of the body, along with its muscles, tendons, bones and attachments, is easy to overlook because it’s out of sight and, therefore, often out of mind. Until, that is, pain occurs. The ischial tuberosity—also known as the “sit bones” or even “sitz bones” (from the German word sitzen) (Garikiparithi 2017)—has many different connections, although it is mainly associated with the hamstring muscles (Drake et al. 2010).
Simplicity Steers Success
client: Jennifer | personal trainer: John Parker | location: San Diego
Keeping it simple. Every day it seems there’s a new supplement, food plan or training program that purports to produce unparalleled results. But all of these choices can make it difficult for clients to make wise choices and remain consistent in their approach. That was the problem faced by Jennifer, a florist and part-time kickboxing instructor, and it’s why she reached out to San Diego–based personal trainer John Parker, CSCS.
Pillars of Functional Training for Active Aging
Healthy aging is more than the absence of disease, according to the World Health Organization (WHO): “For most older people, the maintenance of functional ability has the highest importance” (WHO 2015). Colin Milner, founder and CEO of the International Council on Active Aging in Vancouver, British Columbia, echoes these comments. “When looking at the healthy aging market today, the focus is all about function,” he says.
130/80 = High Blood Pressure
For the first time since 2003, the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have produced a substantial report updating blood pressure recommendations. People with a reading of 130/80 are now classified as having high blood pressure. This is down from 140/90.
According to the ACC, this means 46% of U.S. adults will now be categorized as having hypertension.
Those in the “hypertensive crisis” category require medication intervention and immediate hospitalization if there is organ damage, according to the report.